Ultimate Whey Isolate Coconut
Usually ready in 1 hour —

Ultimate Whey Isolate Coconut
Supports lean muscle growth, shredding & weight management.
The highest dose of pure protein and lowest amount of carbohydrates and fats. Perfect for post-workout or adding to smoothies for an extra protein boost.
Each scoop contains 27.8 grams of fast release protein to help promote muscle repair and recovery and meet your daily protein needs.
Read more Read less
16/5 Scanlon Drive
Epping VIC 3076
Australia
+61392190850
check_circle Pickup available, usually ready in 1 hour




Ingredients
expand_more
Whey Protein Isolate (Milk), Coconut Milk, Natural Flavour, Stevia
ALLERGENS
Contains: milk
Packed under HACCP conditions in a facility that also packs dairy, nuts and dried fruit.
How to use
expand_more
Mix one heaped scoop with 250-300ml of water and shake vigorously. Ideally taken post workout and/or as a snack. Add less or more water to perfect individual sweetness.
Storage: Store sealed in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight below 25 degrees Celsius.
Nutritional info
expand_more
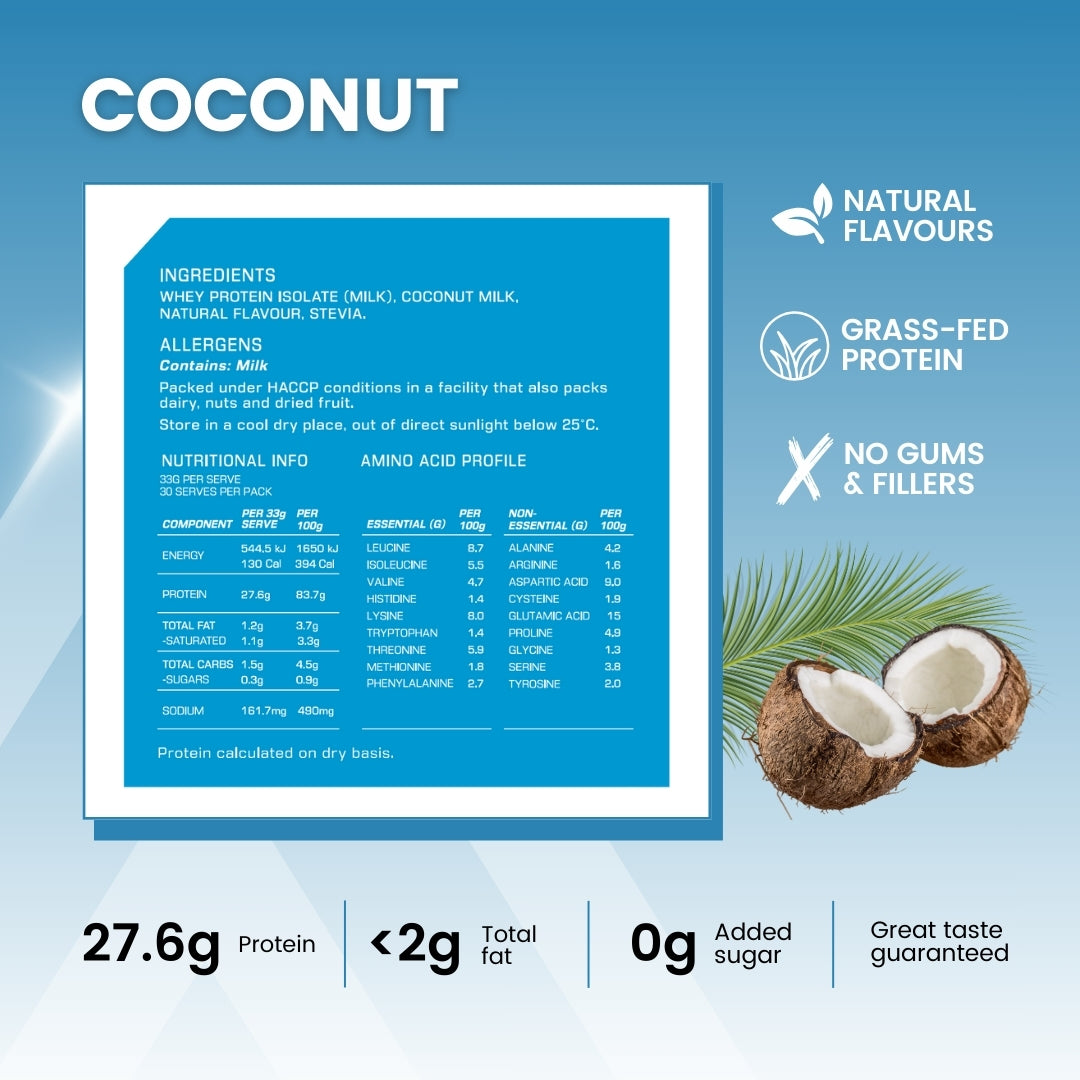
Formulated supplementary sports Food. This product is not a sole source of nutrition and should be consumed in conjunction with a nutritious diet and an appropriate training or exercise program. Not suitable for children under 15 years of age or pregnant women, Should only be used under medical or dietetic supervision.
Benefits
expand_more
- Grass fed fast release Whey protein Isolate
- Supports lean muscle growth, shredding & weight management.
- High absorption rate
- Vegetarian & Keto Friendly
- Immunity Support
- Low in lactose
- Sweetened with natural stevia
- Delicious tasting
- Easy Mixability
Third Party Testing
expand_more
Whey Isolate Heavy Metals Report 06.11.2025
HASTA_Ultimate_Whey_Isolate_Dutch_Chocolate_29.08.2025
Ultimate Whey Isolate Unflavoured microbiology 11.07.2025
Ultimate Whey Isolate Unflavoured Microbiology 29.07.2024
Ultimate Whey Isolate Salted Caramel Microbiology 29.07.2024
Ultimate Whey Isolate Unflavoured Microbials 17.07.2024
Ultimate Whey Isolate Salted Caramel Microbials 17.07.2024
Ultimate Whey Isolate Dutch Chocolate Microbials 26.06.2024
HASTA Ultimate Whey Isolate Dutch Chocolate
Ultimate Whey Isolate Dutch Chocolate Microbiology 13.06.2024
Shipping
expand_more
Same day despatch for orders before 2pm.
FREE SHIPPING ON ORDERS OVER $150
Australia-wide Flat Rate
Shipping - $9.80
(For orders under $150)
Australia-wide Express
Shipping - $14.95 (For
all orders)
You May Also Like
Generic Information and Types:
What is Whey Protein Isolate (WPI)?
expand_more
Whey Protein Isolate or WPI is a very fast-digesting dairy protein that has the highest protein intake per serving with almost no carbohydrates or fats. WPI is also 99% lactose-free, making it suitable for most people who are lactose intolerant.
The process of producing WPI involves filtering the whey to remove most of the fat, lactose, and other non-protein components, resulting in a product with a high protein content. This filtration process usually yields a product that is approximately 90% or more protein, making it one of the purest forms of whey protein available.
Where does Whey Protein come from?
expand_more
Whey protein is a type of protein that is derived from milk. It is a byproduct of the cheese-making process. When milk is coagulated and curdled to make cheese, the liquid portion that remains after the curds are separated is called whey. This whey contains proteins, carbohydrates, fats, vitamins, and minerals.
To produce whey protein powder, the liquid whey is typically filtered to remove most of the carbohydrates, fats, and other non-protein components. The remaining liquid is then processed and dried to create a powdered form of whey protein, which is widely used as a dietary supplement and in various food products.
What is HASTA?
expand_more
In Australia, 'HASTA' stands for the Human and Supplement Testing Australia. It is an independent testing organization that certifies supplements for safety and quality, ensuring they are free from banned substances.
HASTA certification is especially important for athletes who are subject to anti-doping regulations, as it verifies that the supplements they are taking are safe and comply with the standards of sports governing bodies like WADA (World Anti-Doping Agency).
For our full list of products tested by HASTA, click here
Comparisons and Differences:
What is the difference Between Ultimate Whey Isolate and Ultimate Lean Whey?
expand_more
Whey Isolate is a premium form of whey protein, offers the highest protein content per serve and minimal fats and carbs. It is remarkably low in lactose (99% lactose free), making it an excellent choice for individuals with lactose intolerance who struggle with protein digestion.
On the other hand, Lean Protein is a blend of Whey Isolate and whey concentrate, providing slightly less protein per serving and a higher lactose content compared to Isolate. However, it offers a more favourable price point.
What is the difference between Whey Protein and Plant Protein?
expand_more
Whey protein and plant protein are two different types of protein supplements, each derived from distinct sources and offering unique nutritional properties. Here are the key differences between the two:
Source:
- Whey Protein: Whey protein is derived from milk during the cheese-making process
- Plant Protein: Plant proteins are sourced from various plant-based foods, such as peas, soybeans, rice, hemp, chia seeds, pumpkin seeds, and many others.
2. Amino Acid Profile:
- Whey Protein: Whey protein is considered a complete protein, as it contains all nine essential amino acids that the human body cannot produce on its own.
- Plant Protein: Plant proteins, while also containing all nine essential amino acids, are sometimes limited in one or more of them. However, by combining different plant protein sources, individuals can ensure they get a complete amino acid profile.
3. Lactose and Allergen Content:
- Whey Protein: Whey protein contains lactose, a natural sugar found in milk. This can be an issue for people who are lactose intolerant or have a milk allergy.
- Plant Protein: Plant protein is naturally free from lactose and is a suitable alternative for individuals with lactose intolerance or milk allergies.
4. Taste
- Whey Protein: Whey isolate typically has a mild, neutral flavour with a slightly sweet undertone. Additionally, our flavoured varieties of whey isolate are available, offering options like chocolate, vanilla, cookies & cream, salted caramel and more, which can enhance the taste and versatility of the protein powder.
- Plant Protein: Plant proteins typically has a slightly earthy and nutty flavour with a hint of sweetness. Additionally, our flavoured varieties of plant protein are available, offering options like chocolate, vanilla and salted caramel which can enhance the taste and versatility of the protein powder.
What is the difference between Whey Protein and Collagen Protein?
expand_more
Source:
- Whey Protein: Whey protein is derived from milk during the cheese-making process.
- Collagen Protein: Collagen protein is sourced from animal connective tissues, such as skin, bones, and cartilage.
Amino Acid Profile:
- Whey Protein: Whey protein has a well-balanced amino acid profile, including a higher concentration of essential amino acids like leucine, which is crucial for muscle protein synthesis.
- Collagen Protein: Collagen is particularly rich in the amino acids glycine, proline, and hydroxyproline. It lacks some essential amino acids and is not ideal for muscle building.
Digestibility and Benefits:
- Whey Protein: Whey protein is quickly absorbed by the body and is highly bioavailable, making it an excellent choice for post-workout recovery and muscle building.
- Collagen Protein: Collagen is also well-digested and easily absorbed, but its primary benefits are associated with skin, joint, and bone health, as well as hair and nail strength.
Benefits and Uses:
What is the difference between Whey Protein and Collagen Protein?
expand_more
-
Muscle building and recovery: Whey protein is a complete protein, meaning it contains all essential amino acids necessary for muscle growth and repair. It is particularly rich in branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) like leucine, which play a crucial role in stimulating muscle protein synthesis. Consuming whey protein after a workout can aid in muscle recovery and promote muscle mass gain.
-
Weight management: Protein is known to be more satiating than carbohydrates or fats, meaning it can help you feel fuller for longer. By incorporating whey protein into your diet, you may experience reduced hunger and better appetite control, which can contribute to weight management efforts.
-
Supports immune function: Whey protein contains immunoglobulins and lactoferrin, which have immune-enhancing properties. Regular consumption of whey protein may help strengthen the immune system and protect against infections.
-
Antioxidant properties: Whey protein contains certain peptides that have antioxidant effects, helping to neutralize harmful free radicals in the body and reduce oxidative stress.
-
Promotes cardiovascular health: Some studies suggest that whey protein may have a positive impact on cardiovascular health by reducing blood pressure and improving lipid profiles.
-
Blood sugar regulation: Whey protein has been shown to improve insulin sensitivity and help regulate blood sugar levels, making it potentially beneficial for individuals with type 2 diabetes or those at risk of developing it.
-
Supports exercise performance: Due to its role in muscle building and repair, whey protein can also enhance exercise performance and endurance, especially when combined with resistance training.
-
Nutritional convenience: Whey protein is a convenient and easily digestible source of high-quality protein. It can be used in various forms, such as whey protein powders, shakes, or bars, making it a practical option for busy individuals or athletes.
Which Whey Protein is good for Weight Loss?
expand_more
Which Whey protein is best for Muscle gain?
expand_more
Can Whey Protein be used during Pregnancy or breastfeeding?
expand_more
Consumption Timing and Recommendations:
When Whey Protein should be Taken?
expand_more
Here are some common times when whey protein is typically taken:
-
Post-Workout: Consuming whey protein within 30 to 60 minutes after your workout can be beneficial. During this time, your muscles are primed to absorb nutrients, and whey protein provides a fast-digesting source of protein to aid in muscle recovery and repair.
-
Pre-Workout: Some people choose to take whey protein before their workout to provide a readily available source of amino acids during their training session. This can be especially helpful if you're working out in a fasted state or if your meal timing is far from your exercise session.
-
In Between Meals: Whey protein can also be used as a snack between meals to supplement your daily protein intake and keep you feeling full and satisfied.
-
Breakfast: Adding whey protein to your breakfast can be a convenient way to boost your protein intake for the day. It may help with satiety and provide a good foundation for your nutritional needs.
Which Whey Protein is best?
expand_more
When choosing the best whey protein for you, consider the following factors:
-
Protein content: Look for a product with a high percentage of protein per serving.
-
Ingredients: Check the ingredient list for additives, artificial sweeteners, and fillers. Choose products with minimal and natural ingredients.
-
Purity: If you have lactose intolerance or want a product with lower fat and carbohydrates, go for whey protein isolate.
-
Taste and mixability: Read reviews to ensure that the product mixes well and tastes good.
- Price: While cost shouldn't be the sole factor, it's essential to consider your budget.
Which Whey Protein should I buy?
expand_more
-If your goal is to gain lean muscle mass, shredding or weight loss: try using our Ultimate Whey isolate, which has the highest dose of pure protein and lowest amount of carbohydrates and fats and 99% lactose free.
-If your goal is to find something cost-effective to gain lean muscle mass and maintain your daily protein daily and have no issues with lactose: try using our Ultimate Lean Whey which is a 50:50 blend of Whey Isolate and Whey Concentrate. A cost-effective and versatile source of high quality protein.
Mechanism and Nutritional Insights:
How Whey Protein works?
expand_more
Here's how whey protein works:
-
Protein source: As a high-quality protein source, whey protein provides the body with the essential amino acids needed for various physiological functions, including muscle repair, immune system support, enzyme production, and hormone synthesis.
-
Muscle protein synthesis: One of the key mechanisms behind whey protein's popularity in the fitness community is its ability to stimulate muscle protein synthesis (MPS). After intense physical activity or resistance training, muscles experience microscopic damage. Consuming whey protein, especially around the workout window, can trigger MPS, promoting the repair and growth of muscle fibers.
-
Rapid absorption: Whey protein is known for its fast absorption rate, leading to a quick increase in blood amino acid levels. This rapid availability of amino acids allows the body to utilize them for various processes, including muscle repair and growth, faster than other protein sources.
-
Leucine content: Whey protein is particularly high in the amino acid leucine, which plays a crucial role in stimulating muscle protein synthesis. Leucine acts as a signal for MPS, making whey protein an effective choice for those seeking to maximize muscle gains.
-
Appetite control: Protein, in general, is known to promote satiety and help control appetite. Whey protein, due to its rapid digestion and release of amino acids, can contribute to feelings of fullness, which may assist with weight management or weight loss goals.
-
Immune system support: Whey protein contains immunoglobulins and lactoferrin, which are bioactive compounds that support the immune system's function and help protect against infections.
-
Nutritional convenience: Whey protein supplements come in various forms, such as powders and ready-to-drink shakes, providing a convenient and portable way to increase protein intake, especially for those with busy lifestyles or limited access to whole food protein sources.
Is Whey Protein Vegan?
expand_more
No, whey protein is not vegan. Whey is a by-product of the cheese-making process, and it is derived from milk. It contains proteins, primarily whey protein isolate or concentrate. Since milk is an animal product, whey protein is considered non-vegan and not suitable for those following a vegan diet.
Is Whey Protein Keto Friendly?
expand_more
Yes, whey proteins are keto-friendly. The ketogenic diet is a high-fat, moderate-protein, and low-carbohydrate diet that aims to put the body into a state of ketosis, where it burns fat for fuel instead of carbohydrates.
Whey protein, which is derived from milk, is a high-quality protein source with relatively low levels of carbohydrates and fat. It contains essential amino acids, making it a popular choice among fitness enthusiasts and those following low-carb diets, including the ketogenic diet.
Safety and Side Effects:
Is Whey Protein bad?
expand_more
Whey protein is not inherently "bad." In fact, whey protein is a high-quality protein derived from milk during the cheese-making process. It is a complete protein, meaning it contains all essential amino acids that our bodies need.
For many people, including athletes, bodybuilders, and those with certain dietary needs, whey protein can be a convenient and effective way to increase protein intake and support muscle recovery and growth.
Can Whey Protein Cause Acne?
expand_more
There is some evidence to suggest that whey protein may potentially contribute to the development of acne in certain individuals. However, it is essential to understand that the link between whey protein consumption and acne is not definitive and can vary from person to person.
The potential connection between whey protein and acne is attributed to several factors:
-
Hormonal Effects: Too much Whey protein can increase the production of insulin and insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1). Elevated levels of these hormones may influence sebum (oil) production, which can lead to clogged pores and contribute to the development of acne.
-
Dairy Sensitivity: Some individuals may be sensitive to dairy products, including whey protein. Dairy sensitivity can trigger an inflammatory response in the body, which might worsen acne in susceptible individuals.
-
Digestive Issues: Whey protein can be challenging to digest for some people, leading to gastrointestinal disturbances. Digestive problems can also contribute to the development of acne by altering the gut microbiome and potentially leading to systemic inflammation.
-
Dietary Habits: People who consume whey protein supplements might also have other dietary habits that could influence acne, such as consuming large amounts of sugary foods or processed carbohydrates, which can exacerbate skin issues.
It's important to note that not everyone who takes whey protein will experience acne, and some individuals may be able to tolerate it without any adverse effects on their skin.
If you are concerned about whey protein's impact on your skin, consider the following steps:
Consult a Healthcare Professional
Monitor Your Diet
Try alternative protein Sources
Maintain a Healthy Healthcare Routine
Can Whey Protein cause bloating?
expand_more
Whey protein can cause bloating in some individuals. Bloating is a common side effect associated with the consumption of whey protein, especially for those who are lactose intolerant or have a sensitivity to dairy products.
Additionally, some people may be sensitive to certain components of whey protein, such as lactoglobulin or lactalbumin, which can also trigger digestive issues like bloating.
If you experience bloating or other digestive discomfort after consuming whey protein, you may want to consider alternative protein sources such as plant-based protein powders like pea protein, soy protein, or rice protein. Alternatively, you can opt for 99% lactose-free whey protein isolates.
Service Related FAQs
Please refer here
Very smooth to drink good quality protein 👌
A bit too sweet and doesn’t seem to dissolve as well as chocolate flavour
So far so good
It tastes great, so different. But I personally like to change flavours at the end of every packet. I like all the flavours.
Got a weird taste to it.