-
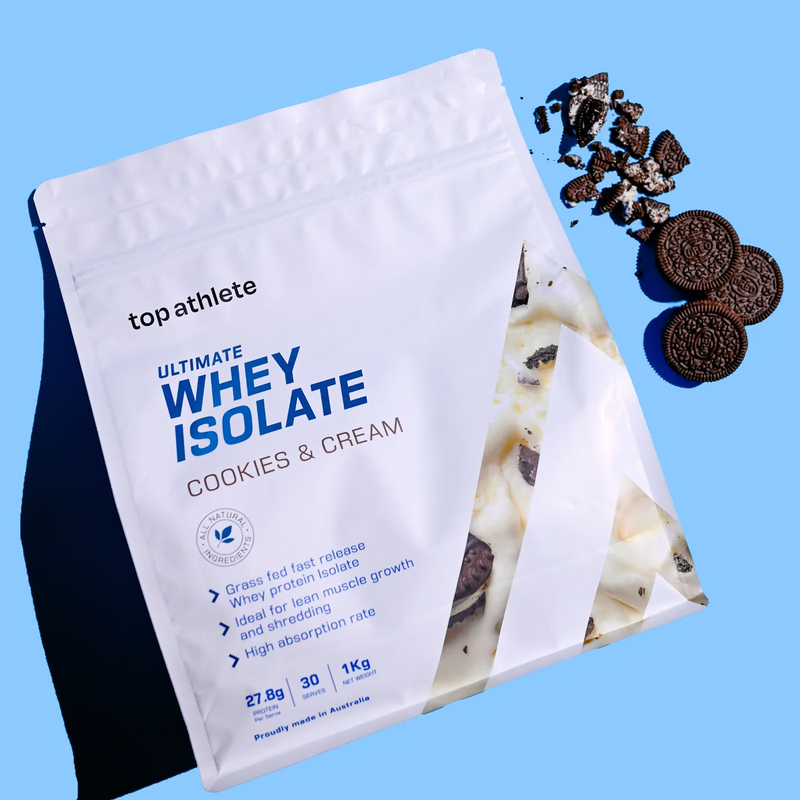
Muscle building and recovery: Whey protein is a complete protein, meaning it contains all essential amino acids necessary for muscle growth and repair. It is particularly rich in branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) like leucine, which play a crucial role in stimulating muscle protein synthesis. Consuming whey protein after a workout can aid in muscle recovery and promote muscle mass gain.
-
Weight management: Protein is known to be more satiating than carbohydrates or fats, meaning it can help you feel fuller for longer. By incorporating whey protein into your diet, you may experience reduced hunger and better appetite control, which can contribute to weight management efforts.
-
Supports immune function: Whey protein contains immunoglobulins and lactoferrin, which have immune-enhancing properties. Regular consumption of whey protein may help strengthen the immune system and protect against infections.
-
Antioxidant properties: Whey protein contains certain peptides that have antioxidant effects, helping to neutralize harmful free radicals in the body and reduce oxidative stress.
-
Promotes cardiovascular health: Some studies suggest that whey protein may have a positive impact on cardiovascular health by reducing blood pressure and improving lipid profiles.
-
Blood sugar regulation: Whey protein has been shown to improve insulin sensitivity and help regulate blood sugar levels, making it potentially beneficial for individuals with type 2 diabetes or those at risk of developing it.
-
Supports exercise performance: Due to its role in muscle building and repair, whey protein can also enhance exercise performance and endurance, especially when combined with resistance training.
-
Nutritional convenience: Whey protein is a convenient and easily digestible source of high-quality protein. It can be used in various forms, such as whey protein powders, shakes, or bars, making it a practical option for busy individuals or athletes.
psychiatry
chevron_left
chevron_right
Clean ingredients
water_full
Easy mixability
task_alt
Gluten-free
package_2
Free delivery over $150
Protein Powder expand_more
-
Whey Protein Isolate
-
Casein Protein
-
Plant Based Protein
-
Collagen Protein
-
HASTA Tested Products
-
All Protein Powders
-
All Top Athlete Supplements
psychiatry
chevron_left
chevron_right
Clean ingredients
water_full
Easy mixability
task_alt
Gluten-free
package_2
Free delivery over $150
Performance & Recovery expand_more
-
Post Workout
-
Fat Burners
-
EAA Sample Packs
-
Creatine Monohydrate
-
View All Performance & Recovery Supps
Apparel expand_more
-
T-shirts
-
Singlets
-
Shorts
-
Hoodies
-
Crew Necks
-
Joggers
-
Heavy Jackets
-
Socks
-
All Apparel